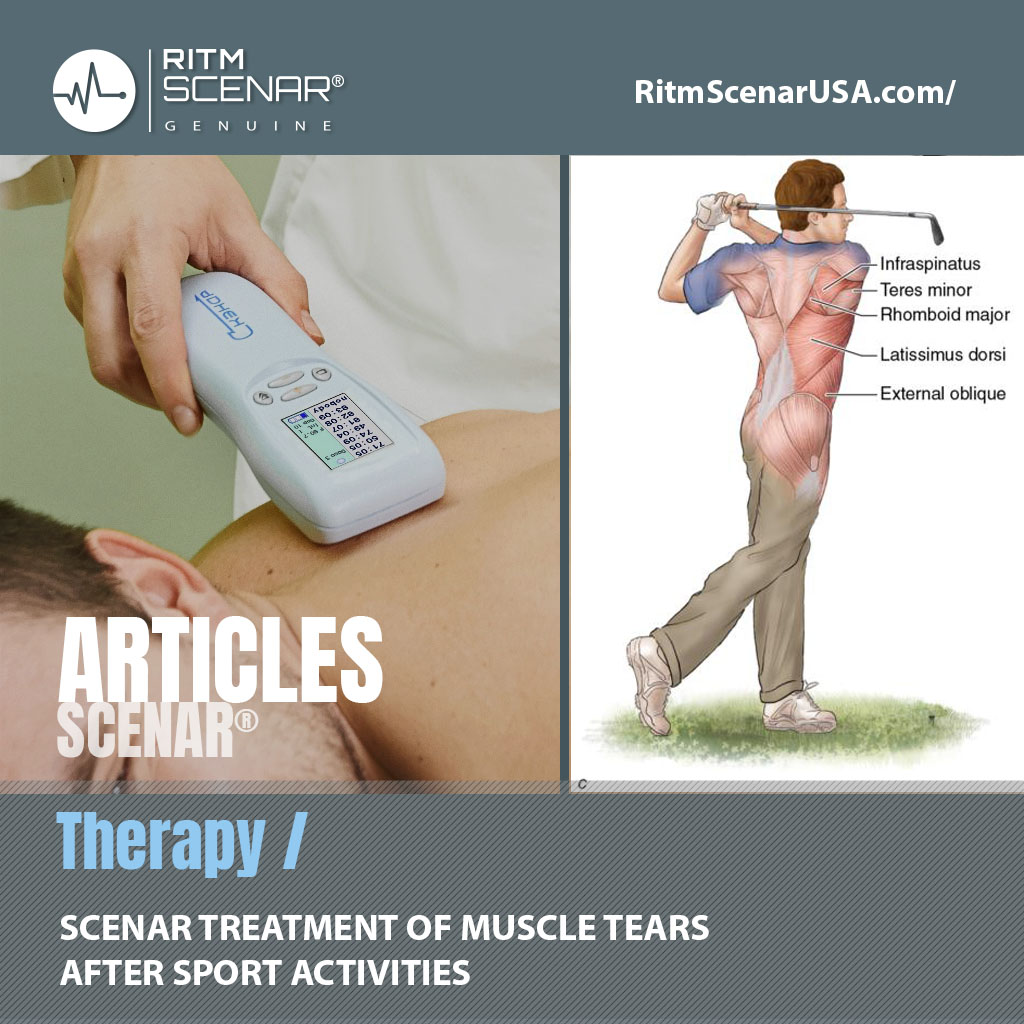
Many sport activities involve precise movement in which muscle groups contract synergistically to achieve the desired effect. Examples are the baseball pitch, the tennis serve, the martial arts roundhouse kick, disc golf throw and the sprint. But perhaps the best example is a golf swing. The golf swing (drive or putt) requires strength, coordination, muscle and soft tissue flexibility, and optimal joint movement in the spine, shoulders, hips, knees, and even ankles.
Any deficiency in one or more of these factors will result in a poor golf swing and poor results (inaccuracy, lack of good distance). Some golfers have trouble swinging due to muscle tension in their backs and shoulders. Shortened muscle fibers do not allow full rotation, and therefore a full and clean swing is difficult to perform.
One reason that can cause this is the buildup of scar tissue in the major muscles used in the golf swing:
- trapezium – rhombuses (connects the shoulder blade to the spine)
- triceps – latissimus dorsi muscle
- quadratus lumborum
- a group of muscles that straighten the spine.
Scar tissue is a matrix of collagen fibers formed in the body in response to a soft tissue injury, repeated micro-tears, and heavy lifting.
So, if you’ve ever been in a car accident (whiplash injury), lifted weights regularly, or performed heavy work for a period of time, chances are you’ve developed a scar tissue in one or more of these muscle groups.
In some cases, it can be felt (palpated) through the skin, feeling like small, hard stones.
How to treat muscle fibrosis
While scar tissue helps repair damaged muscles, it can create its own problems.
Scar tissue does not have contractile properties like muscle fibers. It is not as elastic (stretchable) as a healthy ligament or tendon. And scar tissue fibers are not organized in one direction, such as in muscles, ligaments, tendons, and cartilage. Because of these factors, scar tissue is a “weak spot” that is usually the first to rupture under stress; scar tissue tends to cause “stickiness” between moving structures (adhesions), causing pain and loss of flexibility; and scar tissue, due to its density, can cause regenerated nerve endings to stick together, forming myofascial trigger points.
SCENAR therapy is a pioneer physical therapy method that should be available at any physiotherapy clinic to help relieve pain associated with scar tissue and myofascial trigger points.
Muscle Tears
Immediately after injury:
Apply therapy using D-0 with indicated setting working in the numerical order indicated
Use a combination of brushing, massaging and stationary therapy to locate and change active point
Device settings: F-180Hz, Int-8 or Preset “FastAid”, E – on the border of tolerance.
Treat the most painful place using the built-in electrode.
Treatment time from 5 to 20 minutes, depending on the area.
Repeat the therapy several times a day.
The first 5 days after injury – the focus is on reducing swelling and pain.
Apply therapy to specific muscles using D-0 with indicated setting
- Device settings: FM, Int-5, or Preset “LoFM”, Energy – high, but comfortable.
Treat the regional lymph node with the built-in electrode (30 – 60 seconds), then the injury itself. Then using Conductive gloves, place them on the tendons of the muscles and slowly move along the muscle from the distal to the proximal end in the direction of the lymphatic outflow for 3-5 minutes.
- Device settings: F-30 Hz, Int-8 or Preset “SubAcute”, Energy – high, but comfortable.
Use spaced electrodes (“Pawns”).
Treatment time is from 7 to 20 minutes depending on the size of the muscle.
Starting day 5-6 after the injury, as well as with the “old” injury:
- Treat injured muscles twice: first with the built-in electrode, then with the “Pawns” electrode observing the orientation of the muscle and the direction of the lymph flow.
Device settings: F-40Hz, Int-5 or Preset “MyoUni”. Energy – comfortable.
Treatment time 5-7 minutes.
If a “stickiness” is found that does not change during this treatment, additionally treat this zone until intense hyperemia.
Device settings: F-30Hz, Int-8 or Preset “SubAcute”. Treatment time 2-3 minutes.
- Treat the symmetrical zone.
Device settings: F-60Hz, Int-3 or Preset “Symmetry”. Treatment time 2-3 minutes.
Muscular discomfort.
If you have muscles with signs of myositis (tenderness and increased density) before exercise, the following is recommended:
- Find the most painful point (when palpating) of the muscle, place the electrode on it, and treat for 2 minutes.
Device settings: FM, Int-5 or Preset “HiFM”.
- “Rub” the muscle with the electrode of the device by moving up and down the limb from the center of the muscle to the periphery.
Device settings: F-90Hz, Int-5 or Preset “LocalPain”.
- Place “Pawns” electrode on the tendons of the inflamed muscle.
Device settings: F-30Hz, Int-8 or Preset “SubAcute”.
Increase Energy slowly, until the first sensations of vibration in the muscle. Treat for 3-5 minutes.
SCENAR therapy (in combination with therapeutic and sports rehabilitation) helps:
- shorten the treatment period;
- the athlete continue further training and competition;
- scar revascularization and increase its elasticity;
- accelerat the local metabolism;
- Strengthen the effect of the anti-scar medication.
Medical contributor – B. Kulizhskiy. SCENAR therapist, scientific reader of Deutchen Gesellshaft für Adaptive Terapien e.V. magazine (DEGAT e.V. is a German adaptive therapy society)
List of Reference
- Grinberg J.Z. To a question of the principles of SCENAR-therapy effectiveness “SCENAR-therapy”, “SCENAR-expertise”, collection of articles, issue3-Taganrog, 1997.−pp 16-22.
- Grinberg J.Z. The effectiveness of SCENAR-therapy. Physiological aspects. “SCENAR therapy” and “SCENAR-expertise”. Collection of articles, Issue 4,- Taganrog, 1998.-pp 8-16.
- Kots J.M. – The electrostimulation training of the muscles. – In the book. The materials of scientific – methodical conference on a problem: “Medico-biological ground of the system of students physical training in high school”. – Kaunas, 1975. – pp. 82-84.
- Medvedev S.V. The Application of SCENAR technique in sport medicine. “SCENAR therapy” and “SCENAR-expertise”. Collection of articles, Issue.3.-Taganrog, 1997.-pp60-65.
- Trembach A.B. Marchenko V.V. The characteristics electromiogrammes of weight-lifters biceps at different loads //The theory and practice of physical culture. №8. 2000. Pp.20-22.
- Comparison of the Effectiveness of SMC and SCENAR-Influence in Recovery of the Body Functions of Sportsmen after Training. A. Lopatina PT