Treatment of Intercostal Neuralgia by Non-Invasive Neuroadaptive Physiotherapy
No Comments
Сcontributor: Boris Kulizshkiy,
Deputy Director for Biomedical Affairs, OKB RITM
Intercostal neuralgia or thoracalgia is the second most frequently sought emergency medical care syndrome after acute abdominal pain.
Vertebrogenic thoracalgia (as intercostal neuralgia is called) is a nerve pain in the chest and upper torso that radiates from the upper back. The pain comes from the intercostal nerves along the ribs, chest or abdomen. It may feel like a sharp or stabbing pain, or a burning or aching pain. It may also cause additional symptoms such as numbness and tingling.
A characteristic symptom is an increase in pain when coughing, laughing, moving, bending the body and decreasing at rest and with muscle relaxation. When you take a deep breath, the pain intensifies and “shoots”, which prevents you from taking a full deep breath.
Mostly the pain is localized in the 4-7 intercostal spaces, between the parasternal and anterior axillary lines. Between the ribs there are muscles that contract, the so-called intercostal muscles.
This is a distinctive feature of intercostal neuralgia, which allows it to be differentiated from symptoms of heart disease or other pathologies.
Physiotherapy is recommended in the treatment of intercostal neuralgia. The treatment program will focus on improving the alignment, mobility, and range of motion of the thoracic spine. Methods such as therapeutic electrotherapy will also be used to reduce pain and inflammation of the spinal structures.
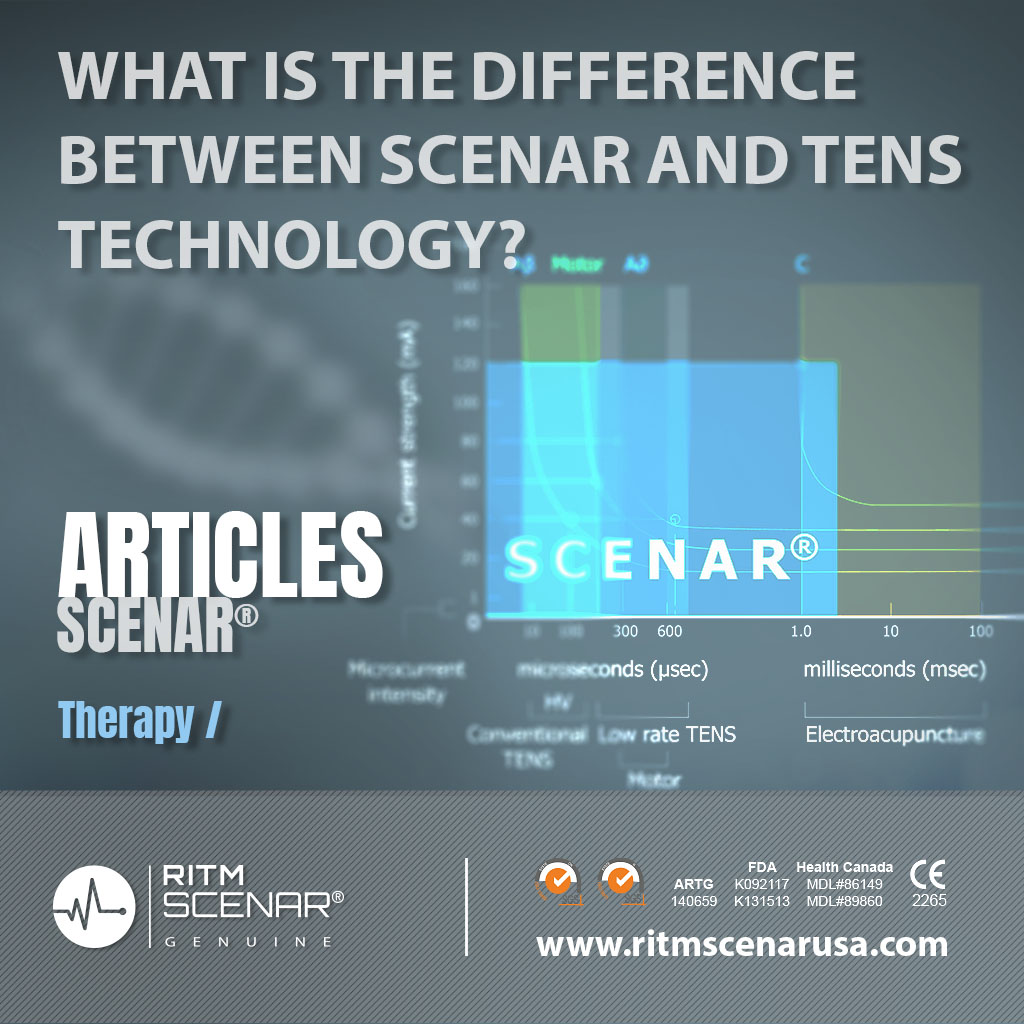
SCENAR is a self-controlled energy-neuroadaptive regulator – a high-tech electrotherapeutic device that has a complex effect of several therapeutic factors and automatically adjusts the therapeutic signal to the patient thanks to feedback.
Conventional therapeutic devices are unidirectional, SCENAR uses active parametric feedback and actively interacts with the processes occurring in the body. The parametric feedback of the SCENAR device controls the impedance of the skin in the sub electrode space and changes the treatment signal as needed. Therefore, maximum therapeutic efficacy can be achieved. Neuroadaptive activation provides immediate analgesia from the first session and a noticeable acceleration of the recovery process, reducing recovery time.
Recommended areas for SCENAR treatment: Acute situation
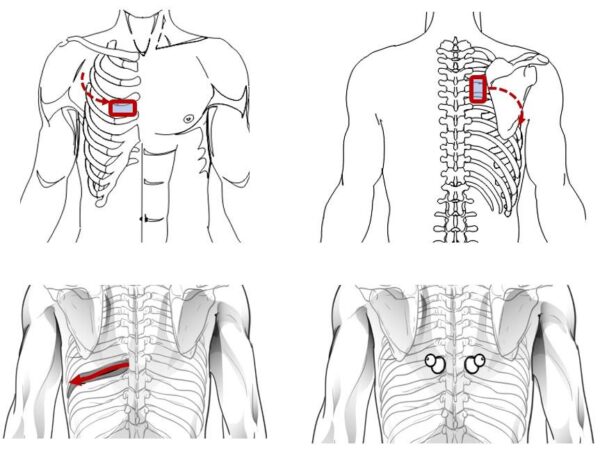
- Place the coaxial electrode of the SCENAR device at the point of maximum pain in the front, asking the patient to point at the most painful place with one finger.
 |
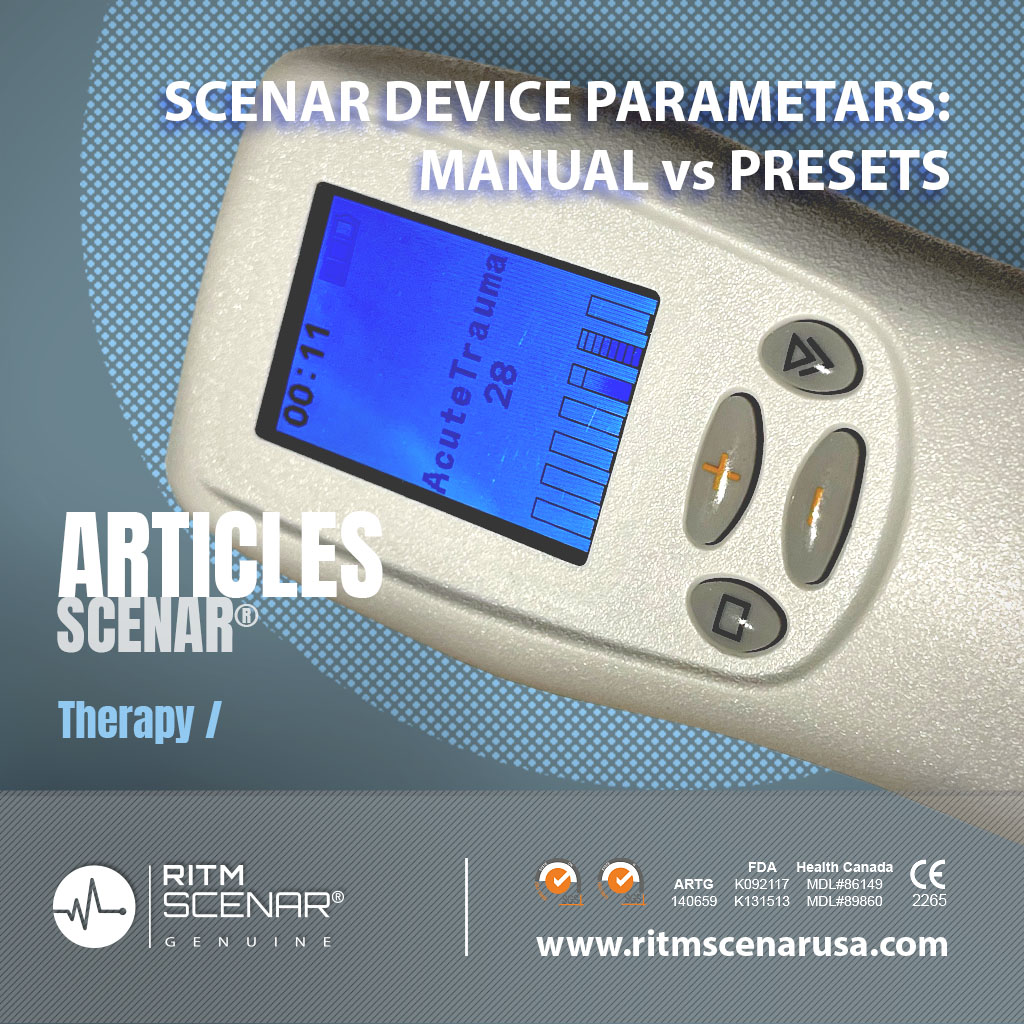
Device settings: F-180Hz, Int-8 or SCENAR FORCE Presets “FastAid” or “AcuteTrauma.
Energy – slightly above comfortable. Time – 3-5 minutes (until the pain disappears). Such pain can migrate to another point during therapy (the patient will immediately say so); the device should be moved to a new point. Apply “Hunt for pain” methos of pain control.
|
After the pain in the periphery has become less intense or decreased, switch on to “Spinal Zone” therapy.
- Start performing SCENAR procedure for “Zones on the spine” with the treatment of the “paravertebral” of the spine.
Treat directly on the spine – the level of complaint formation.
Use “Pawns” electrode. Place them on the paravertebral spine symmetrically at the level corresponding to the intercostal space in which acute pain was detected in the front.
Device settings: FM, Int-5 or SCENAR FORCE Preset “HiFM”. Energy – comfortable.
Built-in electrode can be used. Work for 5-7 minutes. Additionally, treat the intercostal space zone below and above where the affected nerve is located.
- Device settings: F=120Hz, Int-7 or SCENAR FORCE Preset “PoinPain”. and, tightly pressing the built-in electrode to the skin, treat the segment corresponding to the intercostal space from the spine to the chest (as shown in the figure).
When influencing these zones, it is recommended to use both modes:
- D-0 (SDM – subjectively dosed mode)
- D-1 (IDM – individually dosed or digital mode).
Neuroadaptive physical therapy is a non-invasive neuroadaptive modality supported by research, clinical experience and numerous scientific publications. Available technology and high medical benefits and provide the physical therapist with a very specific method of treating the peripheral nervous system and regulating neurovegetative pathways in a non-invasive manner.
Discover a new medical approach to pain, the autonomic nervous system and its clinical and adaptive significance.
REFERENCE LIST:
- The Use of Electronic Biofeedback for the Management of Post-Herpetic Neuralgia – A Report of 3 Cases by Malcolm R. Ing MD.
- A. Volyanik. Experience of using SCENAR-Therapy in the treatment of some pain syndromes in neurology.
- Grinberg Ya.Z. SCENAR therapy: efficiency from the standpoint of electrotherapy methods. //SCENAR therapy, SCENAR examination. Collection of statistics. – Issue 2.
- Revenko A.N. Adaptive regulation (SCENAR). Theoretical and practical justification. //SCENAR therapy, SCENAR examination. Collection of statistics. – Issue 1.
Download PDF version ⬇️ Treatment of Intercostal Neuralgia by Non-Invasive Neuroadaptive Physiotherapy